The Problem
I’m developing the payment of aibeixin app. There is a web hook after payment is done. It carries encrypted data by AEAD_AES_256_GCM algorithm (RFC5116).
I need to:
- Prepare the API Key. [Done]
- Fetch the
nonceandassociated_datafrom the hook request. [Done] - Decrypt the
ciphertext.
I’m building the app with NodeJS.
Asking For Code Generating
I have Codeium (Pro), ChatGPT (3.5) and Claude (Free).
Let me show you how they worked.
Codeium for VSCode
Prompt:
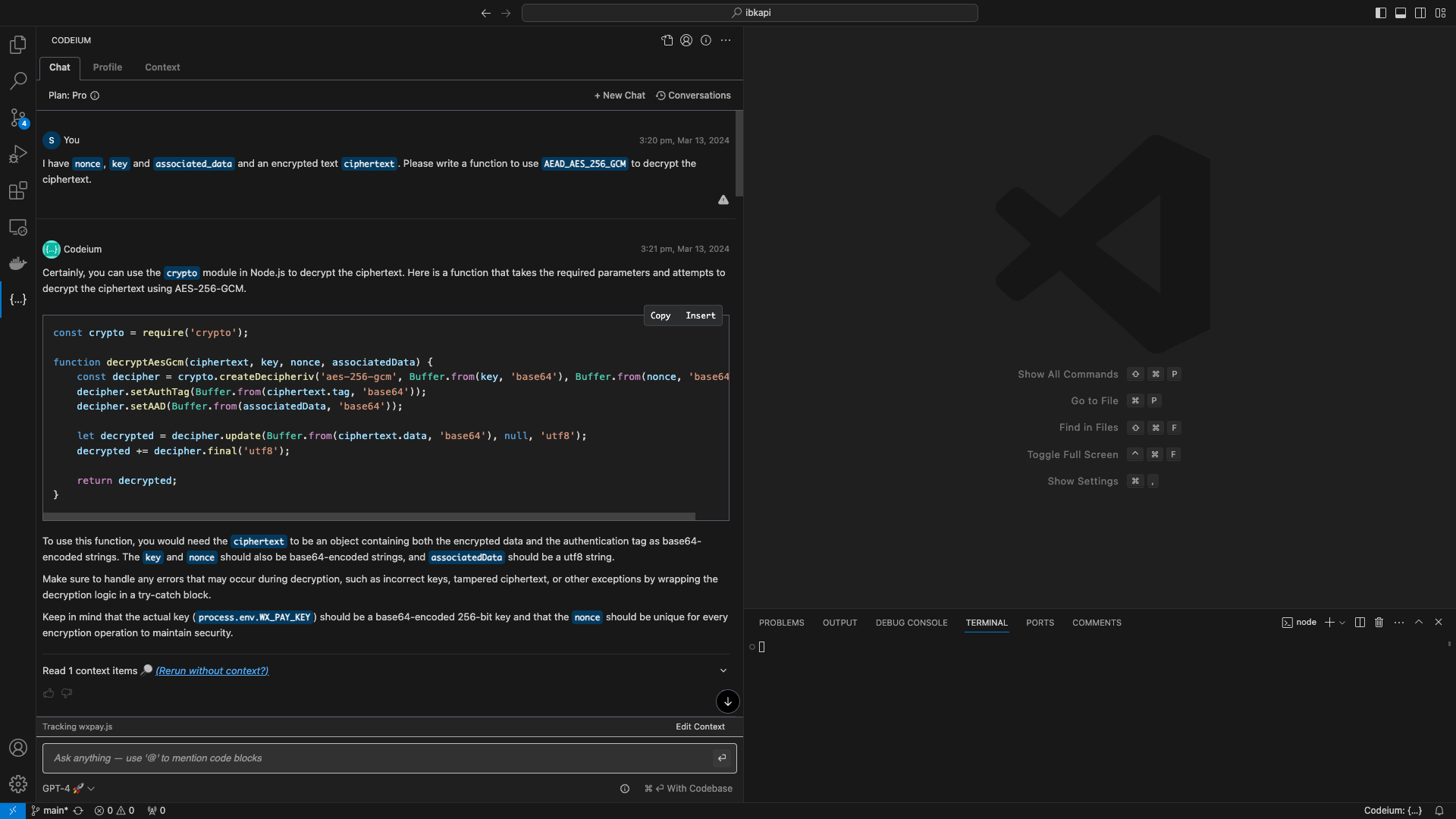
I have
nonce,keyandassociated_dataand an encrypted textciphertext. Please write a function to useAEAD_AES_256_GCMto decrypt the ciphertext.
Response:
Certainly, you can use the
cryptomodule in Node.js to decrypt the ciphertext. Here is a function that takes the required parameters and attempts to decrypt the ciphertext using AES-256-GCM.const crypto = require('crypto'); function decryptAesGcm(ciphertext, key, nonce, associatedData) { const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv('aes-256-gcm', Buffer.from(key, 'base64'), Buffer.from(nonce, 'base64')); decipher.setAuthTag(Buffer.from(ciphertext.tag, 'base64')); decipher.setAAD(Buffer.from(associatedData, 'base64')); let decrypted = decipher.update(Buffer.from(ciphertext.data, 'base64'), null, 'utf8'); decrypted += decipher.final('utf8'); return decrypted; }To use this function, you would need the
ciphertextto be an object containing both the encrypted data and the authentication tag as base64-encoded strings. Thekeyandnonceshould also be base64-encoded strings, andassociatedDatashould be a utf8 string.Make sure to handle any errors that may occur during decryption, such as incorrect keys, tampered ciphertext, or other exceptions by wrapping the decryption logic in a try-catch block.
Keep in mind that the actual key (
process.env.WX_PAY_KEY) should be a base64-encoded 256-bit key and that thenonceshould be unique for every encryption operation to maintain security.
If you want to try Codeium Pro for free with GPT4. Please use my referral link.
ChatGPT 3.5
Chat log:
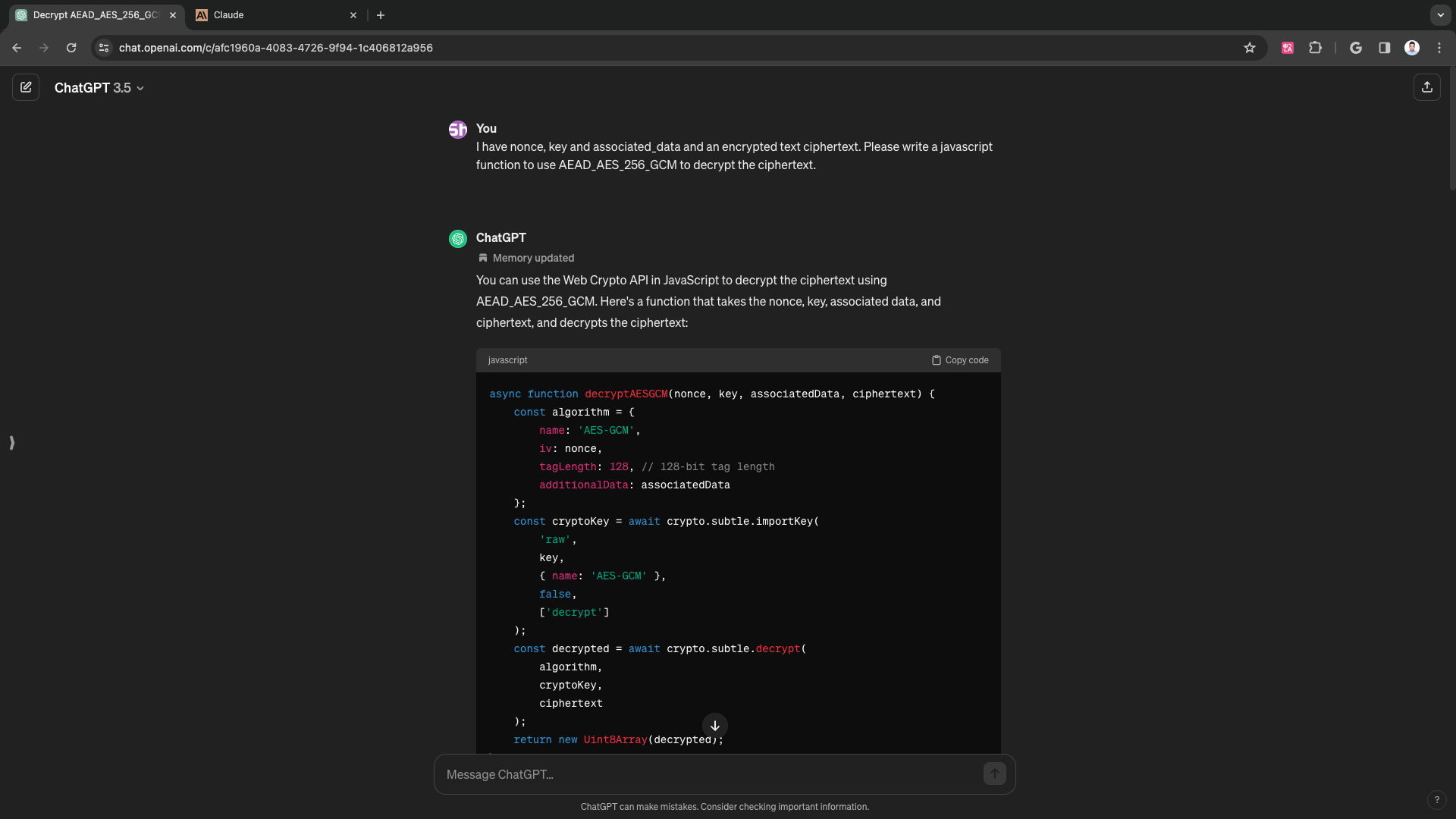
I have nonce, key and associated_data and an encrypted text ciphertext. Please write a javascript function to use AEAD_AES_256_GCM to decrypt the ciphertext.
You can use the Web Crypto API in JavaScript to decrypt the ciphertext using AEAD_AES_256_GCM. Here’s a function that takes the nonce, key, associated data, and ciphertext, and decrypts the ciphertext:
async function decryptAESGCM(nonce, key, associatedData, ciphertext) { const algorithm = { name: 'AES-GCM', iv: nonce, tagLength: 128, // 128-bit tag length additionalData: associatedData }; const cryptoKey = await crypto.subtle.importKey( 'raw', key, { name: 'AES-GCM' }, false, ['decrypt'] ); const decrypted = await crypto.subtle.decrypt( algorithm, cryptoKey, ciphertext ); return new Uint8Array(decrypted); } // Usage example const nonce = new Uint8Array([ /* nonce bytes */ ]); const key = new Uint8Array([ /* key bytes */ ]); const associatedData = new Uint8Array([ /* associated data bytes */ ]); const ciphertext = new Uint8Array([ /* ciphertext bytes */ ]); decryptAESGCM(nonce, key, associatedData, ciphertext).then(plaintext => { console.log('Decrypted plaintext:', plaintext); }).catch(error => { console.error('Decryption error:', error); });Replace the
nonce,key,associatedData, andciphertextarrays with your actual values. This function uses the Web Crypto API’scrypto.subtle.decryptmethod to perform the decryption.
Hmm. It seems not use NodeJS to do that.
I’m using it in Nodejs env
In a Node.js environment, you can use the
cryptomodule to achieve the same encryption and decryption functionality. Here’s how you can decrypt the ciphertext usingcrypto:const crypto = require('crypto'); function decryptAESGCM(nonce, key, associatedData, ciphertext) { const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv('aes-256-gcm', key, nonce); decipher.setAuthTag(ciphertext.slice(-16)); // Last 16 bytes are the authentication tag decipher.setAAD(associatedData); // Set additional authenticated data const plaintext = decipher.update(ciphertext.slice(0, -16)); // Exclude the authentication tag decipher.final(); // Check integrity using the authentication tag return plaintext; } // Usage example const nonce = Buffer.from([ /* nonce bytes */ ]); const key = Buffer.from([ /* key bytes */ ]); const associatedData = Buffer.from([ /* associated data bytes */ ]); const ciphertext = Buffer.from([ /* ciphertext bytes */ ]); const plaintext = decryptAESGCM(nonce, key, associatedData, ciphertext); console.log('Decrypted plaintext:', plaintext.toString());Replace the
nonce,key,associatedData, andciphertextbuffers with your actual values. This function uses Node.js’scrypto.createDecipherivmethod to create a decipher instance with the AES-256-GCM algorithm.
Claude.ai
Prompt:
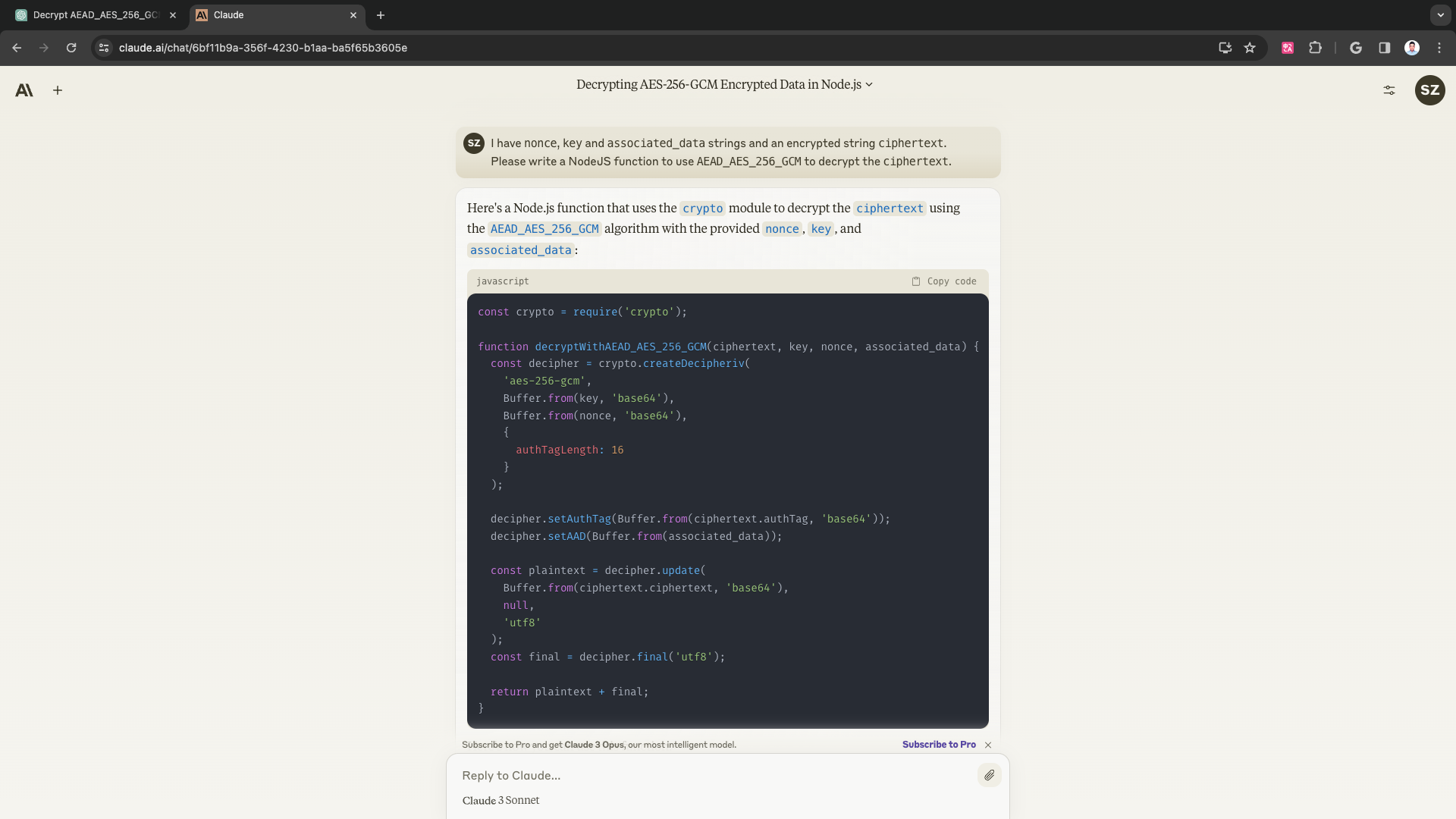
I have
nonce,keyandassociated_datastrings and an encrypted stringciphertext. Please write a NodeJS function to useAEAD_AES_256_GCMto decrypt theciphertext.
Here’s a Node.js function that uses the
cryptomodule to decrypt theciphertextusing theAEAD_AES_256_GCMalgorithm with the providednonce,key, andassociated_data:const crypto = require('crypto'); function decryptWithAEAD_AES_256_GCM(ciphertext, key, nonce, associated_data) { const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv( 'aes-256-gcm', Buffer.from(key, 'base64'), Buffer.from(nonce, 'base64'), { authTagLength: 16 } ); decipher.setAuthTag(Buffer.from(ciphertext.authTag, 'base64')); decipher.setAAD(Buffer.from(associated_data)); const plaintext = decipher.update( Buffer.from(ciphertext.ciphertext, 'base64'), null, 'utf8' ); const final = decipher.final('utf8'); return plaintext + final; }Here’s how you can use this function:
const nonce = 'YOUR_NONCE_STRING'; const key = 'YOUR_KEY_STRING'; const associated_data = 'YOUR_ASSOCIATED_DATA_STRING'; const ciphertext = { ciphertext: 'YOUR_ENCRYPTED_DATA_STRING', authTag: 'YOUR_AUTH_TAG_STRING' }; const decryptedData = decryptWithAEAD_AES_256_GCM( ciphertext, key, nonce, associated_data ); console.log(decryptedData);Here’s how the
decryptWithAEAD_AES_256_GCMfunction works:
- The
crypto.createDecipherivmethod is used to create a decipher instance with theaes-256-gcmalgorithm, the providedkeyandnonce, and anauthTagLengthof 16 bytes.- The
setAuthTagmethod is used to set the authentication tag for the decipher instance using theauthTagproperty of theciphertextobject.- The
setAADmethod is used to set the additional associated data for the decipher instance using the providedassociated_datastring.- The
updatemethod is called with theciphertextproperty of theciphertextobject, and it returns the decrypted plaintext as a buffer.- The
finalmethod is called to get any remaining decrypted data.- The plaintext and the remaining decrypted data are concatenated and returned as a string.
Note that this function expects the
nonce,key,associated_data, andciphertext.ciphertextto be Base64-encoded strings, and theciphertext.authTagto be a Base64-encoded string representing the authentication tag.
The
ciphertextis a single string. please update the function.
Ah, I understand. If the
ciphertextis a single string, we can modify the function as follows:const crypto = require('crypto'); function decryptWithAEAD_AES_256_GCM(ciphertext, key, nonce, associated_data) { const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv( 'aes-256-gcm', Buffer.from(key, 'base64'), Buffer.from(nonce, 'base64'), { authTagLength: 16 } ); const authTag = ciphertext.slice(-32); // Extract the last 32 bytes as the authTag decipher.setAuthTag(Buffer.from(authTag, 'base64')); decipher.setAAD(Buffer.from(associated_data)); const encryptedData = ciphertext.slice(0, -32); // Get the ciphertext without the authTag const plaintext = decipher.update( Buffer.from(encryptedData, 'base64'), null, 'utf8' ); const final = decipher.final('utf8'); return plaintext + final; }Here’s how you can use this updated function:
const nonce = 'YOUR_NONCE_STRING'; const key = 'YOUR_KEY_STRING'; const associated_data = 'YOUR_ASSOCIATED_DATA_STRING'; const ciphertext = 'YOUR_ENCRYPTED_DATA_AND_AUTH_TAG_STRING'; const decryptedData = decryptWithAEAD_AES_256_GCM( ciphertext, key, nonce, associated_data ); console.log(decryptedData);The main changes in the updated function are:
- The
ciphertextis expected to be a single string containing both the encrypted data and the authentication tag.- The last 32 bytes (encoded in Base64) of the
ciphertextare extracted and used as theauthTag.- The
ciphertextwithout the last 32 bytes is used as theencryptedData.This function assumes that the
ciphertextis composed of the encrypted data followed by the authentication tag (32 bytes encoded in Base64). If the format is different, you may need to adjust the code accordingly.
Making It Run
No. None of them can run correctly.
node:internal/crypto/cipher:121
this[kHandle].initiv(cipher, credential, iv, authTagLength);
^
RangeError: Invalid key length
And:
node:internal/crypto/cipher:220
if (!this[kHandle].setAuthTag(tagbuf))
^
TypeError: Invalid authentication tag length: 32
And even:
node:internal/crypto/cipher:193
const ret = this[kHandle].final();
^
Error: Unsupported state or unable to authenticate data
I tried providing errors and asking updates. But all failed.
And then I searched it on Google I found this on StackOverflow.
Here is the final function that can run smoothly:
function decryptAesGcm(ciphertext, key, nonce, associatedData) {
const encryptedBuffer = Buffer.from(ciphertext, 'base64');
const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv('aes-256-gcm', key, nonce);
decipher.setAuthTag(encryptedBuffer.slice(-16)); // Last 16 bytes are the authentication tag
decipher.setAAD(Buffer.from(associatedData)); // Set additional authenticated data
let plaintext = Buffer.concat([
decipher.update(encryptedBuffer.slice(0, -16)),
decipher.final()
]);
return plaintext.toString();
}
Conclusion
You’d check and run several times when using code generated by LLMs. And don’t forget the traditional search engines and communities. Plus, you’d be familiar with the programming language.
Question
What’s your experience when asking LLMs to write code?
Note: Head image generated by Microsoft Copilot. Prompt is: A MacBook on a desk, the screen is showing some codes generated by LLMs and with some errors..
Last modified on March 13, 2024